티스토리 뷰
[Algorithm] 2-5. Recursion 응용 2 - Counting Cells in a Blob
nroo 2018. 1. 11. 04:20Counting cells in a Blob
입력으로 Binary 이미지가 주어진다.
각 픽셀은 background pixel(흰색)이거나 혹은 imagepixel(파란색)이다.
서로 연결된 image pixel들의 집합을 Blob이라고 부른다.
상하좌우 및 대각방향으로도 연결된 것을 Blob으로 간주한다.

따라서 위의 그림에서는 아래와 같은 Blob 집합이 존재한다.
총 4개의 Blob 존재

특정 좌표가 속한 Blob의 크기 count
입력
N * N 크기의 2차원 그리드(grid)
하나의 좌표 (x, y)
출력
픽셀 (x,y)가 포함된 blob의 크기,
(x,y)가 어떤 blob에도 속하지 않는 경우에는 0
Recursive Thinking
현재 픽셀이 속한 Blob의 크기를 카운트하려면
현재 픽셀이 image color가 아니라면
0을 반환한다.
현재 픽셀이 image color라면
먼저 현재 픽셀을 카운트한다 (count=1)
현재 픽셀이 중복 카운트 되는 것을 방지하기 위해 다른 색으로 칠한다.
현재 픽셀에 이웃한 모든 픽셀들(8개 픽셀들) 각각에 대해서
그 픽셀이 속한 Blob의 크기를 카운트하여 카운터에 더해준다.
카운터를 반환한다.
순환적 알고리즘 - 1
x=5, y=3이라고 가정, 즉 이 픽셀이 포함된 blob의 크기를 계산하는 것이 목적이다.
count=0에서 시작.
다음으로 현재 cell을 다른색으로 칠하고 count를 1증가한다. 이렇게 색칠하는 것은 이 픽셀이 중복 count 되는 것을 방지하기 위해서 이다.
현재 count=1
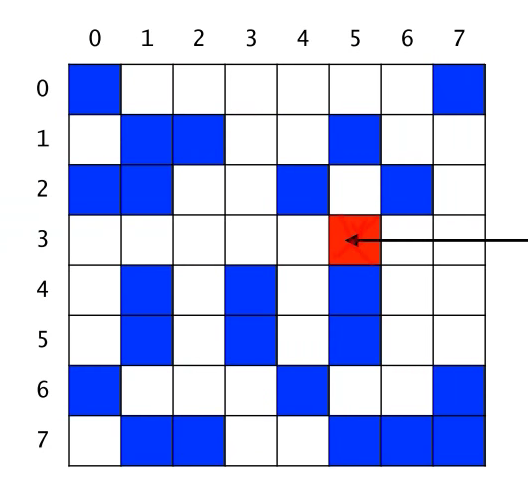
그 다음 (5, 3)픽셀에 인접한 8개의 픽셀에 대해서 순서대로 그 픽셀이 포함된 Blob의 크기를 count한다. 북, 북동, 동, 동남, .. 순으로 고려한다.
가장 먼저 북쪽인(5,2) 픽셀이 포함된 Blob의 크기는 0이다. 따라서 count 값은 변화없이 1이다.
다음으로 북동쪽인(6,2) 픽셀이 속한 Blob을 count하고, count된 픽셀들을 빨간색으로 색칠한다.
여기서 보면(6,2) 픽셀을 포함한 Blob의 count는 3이다. (6,2), (6,2)의 북서쪽인 (5,1), (5,1)의 남서쪽인 (4,2) 총 3개이다.
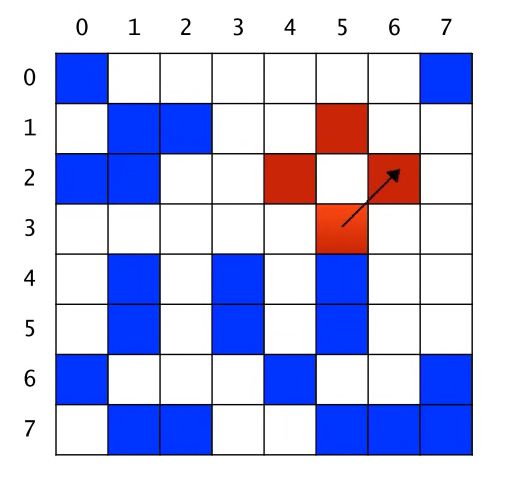
현재 count = 1 + 3 = 4
카운트 된 모든 픽셀들은 빨간색으로 칠해져서 중복카운트 방지
동일한 방법으로 다음 순서에 해당하는 남쪽 픽셀(5,4)이 속한 Blob의 크기는 9이다. 카운트 하고 색칠한다.
count = 4 +9 = 13

남서, 서, 북서 방향은 픽셀이 속한 Blob이 없거나 혹은 이미 카운트 되었기 때문에 count에 영향을 주지 않는다.
결과적으로 count 값 13 return.
Algorithm for countCells(x, y)
if the pixel (x, y) is outside the grid
the result is 0;
else if pixel (x, y) is not an image pixel or already counted
the result is 0;
else
set the color of the pixel (x, y) to a red color
the result is 1 plus the number of cells in each piece of the Blob that includes a nearest neighbour;Java Code 구현
x = 열, y = 행
public class CountingCellsBlob {
private static int BACKGROUND_COLOR = 0;
private static int IMAGE_COLOR = 1;
private static int ALREADY_COUNTED = 2;
private static int N = 8;
private static int[][] grid = {
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1},
};
public static int countCells(int x, int y) {
if (x < 0 || x >= N || y < 0 || y >= N)
return 0;
else if (grid[x][y] != IMAGE_COLOR)
return 0;
else {
grid[x][y] = ALREADY_COUNTED;
return 1 + countCells(x, y + 1) + countCells(x + 1, y + 1)
+ countCells(x + 1, y) + countCells(x + 1, y - 1)
+ countCells(x, y - 1) + countCells(x - 1, y - 1)
+ countCells(x - 1, y) + countCells(x - 1, y + 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
printGrid();
int blobCount = countCells(3, 5);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("BlobCount : " + blobCount);
printGrid();
}
private static void printGrid() {
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++) {
System.out.print("[");
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
System.out.print(grid[x][y] + ", ");
System.out.println("]");
}
}
}
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, ]
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, ]
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, ]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, ]
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, ]
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, ]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, ]
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, ]
BlobCount : 13
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, ]
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, ]
[1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, ]
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, ]
[0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0, ]
[0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0, ]
[1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, ]
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 2, 2, ]
Process finished with exit code 0'ICT Eng > Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] 2-7. Recursion 응용 4 - 멱집합, PowerSet (0) | 2018.01.14 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] 2-6. Recursion 응용 3 - N Queens Problem(Backtracking) (0) | 2018.01.14 |
| [Algorithm] 2-4. Recursion 응용 1 - 미로찾기 Java 구현 (0) | 2018.01.11 |
| [Algorithm] 2-3. 순환의 개념과 기본 3 - Designing Recursion (0) | 2018.01.09 |
| [Algorithm] 2-2. 순환의 개념과 기본 2 - Recursive Thinking (0) | 2018.01.09 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- IT융합인력양성사업단
- 레드블랙트리
- 순환
- github
- 스프링부트
- 라즈베리파이
- Algorithm
- Recursion
- ORM
- 한밭이글스
- AWS
- Spring
- Spring Boot
- Vue.js
- vuejs
- RBT
- springboot
- 인프런
- 자바
- 시간복잡도
- Java
- 정렬
- 젠킨스
- JPA
- vuex
- 무선통신소프트웨어연구실
- Wisoft
- 알고리즘
- 한밭대학교
- Raspberry Pi
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
